Rollup stacks
If you're a developer and want to know what the benefits of modular blockchains are for you, you’ve come to the right place. This page will give you the rundown on modular blockchains and their benefits for developers like you.
This section provides various guides and tutorials that cover different options for deploying rollups on Celestia.
Quickstart - Building on Celestia
Choose a framework
So, you’re ready to start experimenting and building on Celestia? Here are a few options that are currently available for developers.
Rollups as a Service
Deploy your rollup with a RaaS provider.
Smart contracts
Deploy your smart contracts on dedicated EVM-compatible rollups.
What is a rollup?
A rollup is a type of blockchain that offloads some work to a layer 1, like Celestia. Rollups host applications and process user transactions. Once those transactions get processed, they are then published to layer 1. It’s layer 1s job to order those transactions and check that they are available, at minimum.
What is a modular blockchain?
With blockchains there are more or less four core functions that they do.
- Execution: transaction execution and state update.
- Settlement: finality and dispute resolution.
- Consensus: agreement on transaction ordering.
- Data availability: prove data was published to the network.
Modular blockchains specialize in one or two of these functions rather than doing all of them like a monolithic blockchain. You probably know about layer 1s and layer 2s. That’s the general idea.
A typical example of a modular blockchain you might’ve heard of is a rollup. Rollups host smart contracts and execute transactions, much like any monolithic chain. But, the data of those transactions get sent to a layer 1 blockchain to carry out the remaining functions.
If you want to brush up on your understanding of modular blockchains, head over to learn modular.
Benefits of modular blockchains
Ease of deploying a chain
One of the goals of modular blockchains is to make it as easy to deploy a blockchain as a smart contract. There are a few unique ways that modular blockchains can significantly reduce the cost of deploying a new blockchain.
- No validator set is required. Rollups can deploy without sourcing their own set of validators or sequencers.
- Inherit security from the start. Rollups don’t need to build all their security from scratch.
- Any part of the stack can be delegated. Development time can be reduced by outsourcing functions of the rollup to external providers.
All in all, builders will be able to outsource as much of the stack as they need. Deploying a new blockchain will be as simple as clicking a few options to initialize a production-ready rollup.
Scaling
Of course, a much higher scale is necessary if we want to support many more users. And modular blockchains use some new innovative technologies that can help us get there.
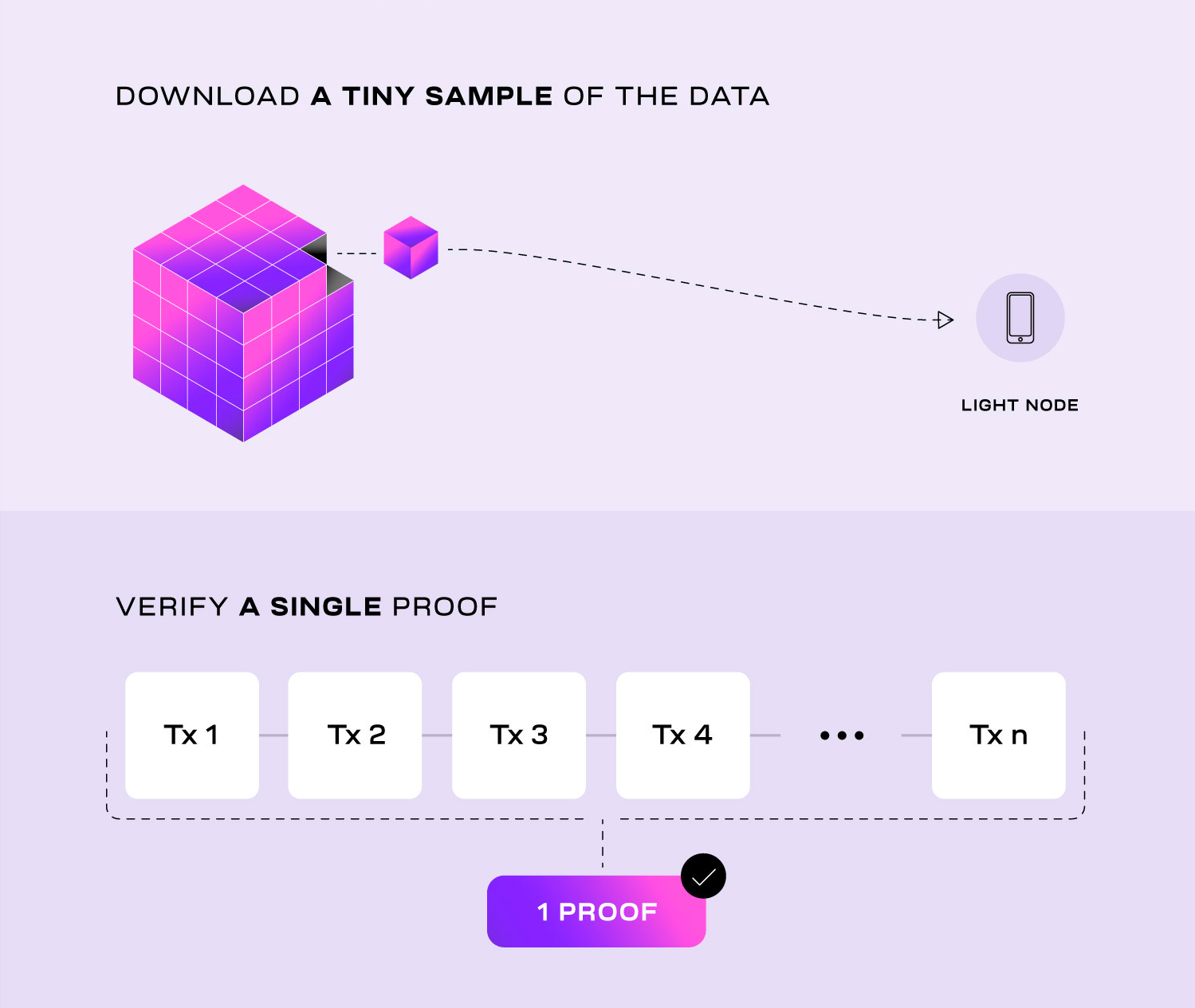
- Data availability sampling enables modular blockchains like Celestia to scale data availability with the number of light nodes - that means more capacity for rollups.
- Fraud and validity proofs make rollups vastly more efficient to verify. Nodes only need to verify a small proof of transaction validity (validity proof) or assume transactions are valid by default (fraud proof). This means rollups don’t require every node in the network to re-execute every transaction.
- Decoupling execution from consensus lets developers define the VM that best fits the scaling needs of their application.
- Separating applications across multiple rollups isolates congestion. If an application congests the execution capacity of one rollup, all other rollups remain unaffected in their execution capacity.
All these scaling properties combined make new types of applications and features possible, like onchain gaming, dynamic metadata, and ephemeral rollups, to name a few.
Customizability
By design, modular blockchains don’t lock in any feature set. They promote experimentation and customization.
Remember how decoupling execution from consensus enables VM customizability? Well, rollups are the execution component. Applications can run on their own rollup and adjust the VM to maximize their application's performance. Developers have that flexibility because Celestia's execution logic doesn't restrict rollups.
Basically, rollups can be customized to integrate any new or existing VM stack.
With existing rollup frameworks, developers can run rollup testnets using the EVM or Cosmos SDK. In the future, one can imagine a variety of VMs that rollup frameworks support, providing developers with more out-of-the-box options for their applications.
Some customizations that could be made to a rollup's VM include custom precompiles, changing transaction processing from sequential to parallel, or adding support for private smart contracts.
All of this only scratches the surface.